Topics & Resources media
Technical Interconnection, Codes ... Utility Interconnection Process
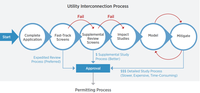
Interconnecting distributed PV onto a grid safely, reliably, and cost-effectively requires that utilities and customers must follow specific rules, procedures, and agreements. Interconnection standards and codes are typically a multi-step process that dictate where and how DPV can be connected to the grid (see figure below). In some cases, smaller, simple DPV systems may be eligible for an expedited (i.e. “fast-track”) review process. Technical screens are a set of basic questions that identify if a DPV system poses grid safety or reliability concerns. Larger systems that do not fit requirements or pass screens may have to be studied in detail to determine grid impacts and mitigation strategies. Interconnection standards are typically followed by a permitting process managed by a local jurisdiction. Equipment standards dictate the requirements of DPV components (e.g. inverter) to maintain system reliability.
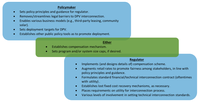
Role of Policymaker and Regulator for DPV
Regulators and policymakers play important roles when it comes to DPV programs. Regulators govern the utility industry by setting standards (e.g. interconnection), determining revenues, calculating tariffs to recover costs, overseeing planning, and other conducting other activities that are intimately connected to DPV deployment. Policymakers, in turn, have multiple public policy tools available to target DPV barriers to adoption and enable market growth. In some cases, policymakers and regulators may have overlapping roles when it comes to DPV.